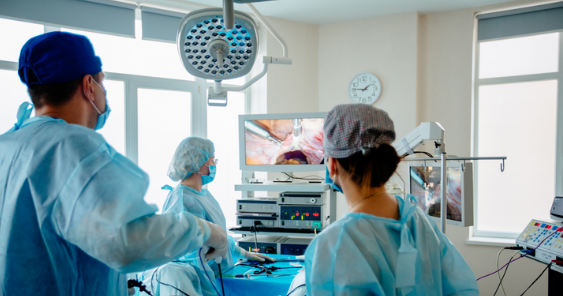
Hysteroscopy Surgery is a minimally invasive procedure used to examine and treat problems inside the uterus. It involves inserting a thin, lighted instrument called a hysteroscope through the vagina and cervix into the uterus, allowing the doctor to view the uterine lining in detail. Hysteroscopy can be diagnostic or operative—used to identify issues like abnormal bleeding, fibroids, or polyps, or to perform treatments like removing adhesions or retrieving lost IUDs. The procedure is usually done on an outpatient basis, with minimal discomfort and a quick recovery time. It provides a safe and effective way to manage various gynecological conditions without the need for major surgery.
Health Care Plans.
- Minimally invasive procedure to examine the uterus
- Uses a thin hysteroscope inserted through the cervix
- Helps diagnose and treat uterine conditions
- Commonly used for fibroids, polyps, and abnormal bleeding
- Usually performed without incisions
- Quick procedure with same-day discharge
- Minimal pain and fast recovery
FAQs
Hysteroscopy is a procedure that allows doctors to look inside the uterus using a thin, lighted tube to diagnose or treat problems.
It is used to investigate abnormal bleeding, remove fibroids or polyps, treat uterine adhesions, or retrieve an IUD.
The procedure is usually well-tolerated. It may cause mild cramping, and local or general anesthesia may be used depending on the case.
Most hysteroscopies take 15 to 30 minutes and are done as outpatient procedures, allowing you to go home the same day.
Recovery is usually quick—most women resume normal activities within 1–2 days.
It is generally safe, but like any procedure, there is a small risk of infection, bleeding, or uterine perforation.